17CS33 Module 1 notes
Click on below Syllabus to view module 1( 17cs33)notes
Array. Structure & Unions. Pointer and Dynamic memory allocation function. Representation of Linear Arrays in Memory, Dynamically allocated arrays, Array Operations: Traversing, inserting, deleting, searching, and sorting. Multidimensional Arrays, Polynomials and Sparse Matrices. Strings: Basic Terminology, Storing, Operations and Pattern Matching algorithms
Introduction
Data Structure is a way of collecting and organising data in such a way that we can perform operations on these data in an
effective way. Data Structures is about rendering data elements in terms of some relationship, for better organization and storage. For example, we have some data which has, player's name and age. Here is of String data type and is of integerdata type.
effective way. Data Structures is about rendering data elements in terms of some relationship, for better organization and storage. For example, we have some data which has, player's name and age. Here is of String data type and is of integerdata type.
What is Data Structure?
1. A data structure is a systematic way of organizing and accessing data.
- A data structure tries to structure data!
- U sually more than one piece of data
- Should define legal operations on the data
- The data might be grouped together (e.g. in an linked list)
- When we define a data structure we are in fact creating a new data type of our own.
- i.e. using predefined types or previously user defined types.
Such new types are then used to reference variables type within a program
Advantages:-
1) Allows easier processing of data.
2) It allows information stored on disk very efficiently.
3) These are necessary for designing an efficient algorithm.
4) It provides management of databases like indexing with the help of hash tables and arrays.
5) We can access data anytime and anywhere.
6) It is secure way of storage of data.
7) Graphs models real life problems
8) It allows processing of data on software system
Disadvantages:-
1) It is applicable only for advanced users.
2) If any issue occurs it can be solved only by experts.
3) Slow access in case of some data types
Practical use of data structure:
For fast data lookup, data indexing, Ip addressing, parsers, dynamic memory allocation,process scheduling,dictionary, directory traversal,web crawling , organizing file hierarchy etc.
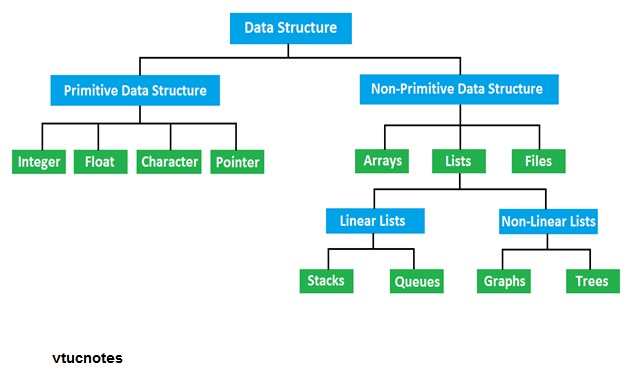
Classification of data structure :
The classification of data structure mainly consists of :
1. Primitive data structure
2. Non-primitive data structure
Integer (int)
· A whole number without any decimal point is called integer .
· Int is keyword to declare integer.
· It allocate 2 bytes of memory
Syntax int variable list;
Ex int a; // a is valid variable declaration
A=10 // initialization of variable
types of int
types of int
- short int
- long int
- long long int
Type
|
Size(bytes)
|
Range
|
int or signed int
|
2
|
-32,768 to 32767
|
unsigned int
|
2
|
0 to 65535
|
short int or signed short int
|
1
|
-128 to 127
|
unsigned short int
|
1
|
0 to 255
|
long int or signed long int
|
4
|
-2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647
|
unsigned long int
|
4
|
0 to 4,294,967,295
|
Short int : It allocate 1 byte of memory
syntax : short int variable ;
ex short int b;
long int : To increase the size of memory allocation from 2 byte to 4 byte use long int
syntax : long int variable;
ex: long int d;
long long int : To increase the size of memory allocation from 4 byte to 8byte use long int
syntax :long long int variable;
ex:long long int e;
Floating point number (float)
· A whole number with any decimal point is called floating point number.
· float is keyword to declare floating point number.
· It allocate 4 bytes of memory.
after decimal point it allow 6 digit number
Ex float z; // zis valid variable declaration
Type
|
Storage size
|
Value range
|
Precision
|
float
|
4 byte
|
1.2E-38 to 3.4E+38
|
6 decimal places
|
double
|
8 byte
|
2.3E-308 to 1.7E+308
|
15 decimal places
|
long double
|
10 byte
|
3.4E-4932 to 1.1E+4932
|
19 decimal places
|
Character type
Character types are used to store characters value.
Size and range of Integer type on 16-bit machine
Type
|
Size(bytes)
|
Range
|
char or signed char
|
1
|
-128 to 127
|
unsigned char
|
1
|
0 to 255
|
Syntax : char variable ; ex char name ;//name=’a’; or name =”adarsh”
void type means no value. This is usually used to specify the type of functions which returns nothing. We will get acquainted to this datatype as we start learning more advanced topics in C language, like functions, pointers etc.Example of Non-primitive data structure :
-
Arrays
-
Lists
-
Files
Arrays :
Arrays are the set of homogeneous data elements
stored in RAM. So, they can hold only one type of data. The data may
be all integers, all floating numbers or all characters. Values in an
array are identified using array name with subscripts. Single
sub-scripted variables are known as a one-dimensional array
or linear array; two sub-scripted variables are referred as a
two-dimensional array.
Lists :
A list is a collection of a variable number of
data items. Lists fall in the non-primitive type of data structure in
the classification of data structure. Every element on a list
contains at least two fields, one is used to store data and the other
one is used for storing the address of next element.
Files :
Files
contain data or information, stored permanently in the secondary
storage device such as Hard Disk and Floppy Disk. It is useful when
we have to store and process a large amount of data. A file stored in
a storage device is always identified using a file name
like HELLO.DAT
or TEXTNAME.TXT and
so on. A file name normally contains a primary and a secondary name
which is separated by a dot(.).
Stack :
Like arrays, a stack is also defined as an ordered collection of elements. A stack is a non-primitive linear data structure having a special feature that we can delete and insert elements from only one end, referred as TOP of the stack. The stack is also known as Last In First Out (LIFO) type of data structure for this behaviour.
Queues :
Queues
are also non-primitive linear data structure. But unlike stacks,
queues are the First In First Out (FIFO) type of data structures. We
can insert an element in a queue from the REAR end but we have to
remove an element from the only FRONT end.
Trees :
Trees
fall into the category of non-primitive non-linear data structures in
the classification of data structure. They contain a finite set of
data items referred as nodes. We can represent a hierarchical
relationship between the data elements using trees.
Graph :
Graph
falls in the non-primitive non-linear type of data structure in the
classification of data structure. Graphs are capable of representing
different types of physical structures. Apart from computer science,
they are used broadly in the fields of Geography, Chemistry &
Engineering Sciences.