Pointer
Pointer
Pointer is variable which hold the address of a variable
Pointer declaration :
It is similar to normal variable declaration only difference is variable contain * symbol before variable name
Syntax data type *pointer variable name
Where * : asterisk
Data type : Basic data type like int, float, char, double
Pointer variable name is valid identifier
Example
int *i; /* pointer to an integer */
double *d; /* pointer to a double */
float *f; /* pointer to a float */
char *c /* pointer to a character */
Initialization of Pointer variable
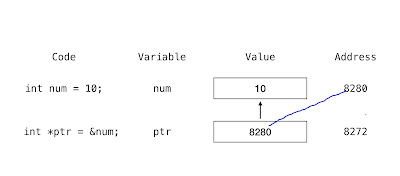
Pointer Initialization is the process of assigning address of a variable to a pointer variable. Pointer variable can only contain address of a variable of the same data type. In C language address operator & is used to determine the address of a variable. The & (immediately preceding a variable name) returns the address of the variable associated with it.
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int a = 10;
int *ptr; //pointer declaration
ptr = &a; //pointer initialization
}
Pointer variablea always point to variables of same datatype. Let's have an example to showcase this:
Example 2
Output
function in pointer
Definition a small code is written separately whenever code is required called and executed is called function.
syntax of function
data type function_name( parameter list)
{
body of function
}
in these function we are passing address of variable instead of value through pointer . Any changes made in function will effect
example call by pointer value
#include<stdio.h>
void add(int ,int);// function prototype
void main()
{
int a=5,b=6;
int *p,*q; // pointer variable
p=&a; // assign the address of variable a to pointer variable p
q=&b;//assign the address of variable b to pointer variable q
add(*p,*q);
}
void add(int *p,int *q)
{
int sum=0;
sum=*p+*q;
printf("sum of two number =%d",sum);
}
example 2 swapping of two number using intermediate variable
#include<stdio.h>
void add(int ,int);// function prototype
void main()
{
int a=10,b=20;
int *p,*q; // pointer variable
p=&a; // assign the address of variable a to pointer variable p
q=&b;//assign the address of variable b to pointer variable q
printf(" Before swapping a=%d & b=%d ",a,b);
swap(*p,*q);
}
void swap(int *p,int *q)
{
int *temp;
temp=p;
p=q;
q=temp;
printf("After swapping a=%d & b=%d ",p,q);
}
output
Before swapping a=10 & b=20
After swapping a=20 & b=10
example 2 swapping of two number without using intermediate variable
#include<stdio.h>
void add(int ,int);// function prototype
void main()
{
int a=10,b=20;
printf(" Before swapping a=%d & b=%d ",a,b);
swap(&a,&b); //call by Address
}
void swap(int *p,int *q)
{
*p=*p+*q;
*q=*P-*q;
*p=*P-*q;
printf("After swapping a=%d & b=%d ",p,q);
}
output
Before swapping a=10 & b=20
After swapping a=20 & b=10
Example 2
Advantage of pointer
1) Pointer reduces the code and improves the performance, it is used to retrieving strings, trees etc. and used with arrays, structures and functions.
2) We can return multiple values from function using pointer.
3) It makes you able to access any memory location in the computer's mem
/*C
program to create, initialize, assign and access a pointer variable.*/
#include
<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int num; /*declaration of integer variable*/
int *pNum; /*declaration of integer pointer*/
pNum=& num; /*assigning address of
num*/
num=100; /*assigning 100 to variable num*/
//access
value and address using variable num
printf("Using variable num:\n");
printf("value of num: %d\naddress of num: %u\n",num,&num);
//access
value and address using pointer variable num
printf("Using pointer variable:\n");
printf("value of num: %d\naddress of num: %u\n",*pNum,pNum);
return 0;
}
Using variable num:
value of num: 100
address of num: 2764564284
Using pointer variable:
value of num: 100
address of num: 2764564284
Pointer & Array
Array is a collection of similar data element
Ex int arr[5] = { 11, 22, 33, 44, 55 };
Assuming the base address of arr is 1000 and each integer requires two bytes, the five elements will be stored as follows:
Element arr[0] arr[1] arr[2] arr[3] arr[4]
11
|
22
|
33
|
44
|
55
|
Address 1000 1002 1004 1006 1008
pointer p
1000
|
Pointer variable p holds the address of array ie arr[0].
We can write it as
int *p; //pointer variable
int arr[5]={11,22,33,44,55};
p=&arr; //or
p=&arr[0];
Example write a c program that print array element using pointer
#include <stdio.h>
main () {
int arr[3] = {5, 10, 15};
int i, *ptr[3];
for ( i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
ptr[i] = &arr[i]; /* assign the address of integer. */
}
for ( i = 0; i < arr; i++) {
printf("Value of arr[%d] = %d\n", i, *ptr[i] );
}
}
Out put
Value of arr[0] = 5
Value of arr[1] = 10
Value of arr[2] = 15
Definition a small code is written separately whenever code is required called and executed is called function.
syntax of function
data type function_name( parameter list)
{
body of function
}
in these function we are passing address of variable instead of value through pointer . Any changes made in function will effect
example call by pointer value
#include<stdio.h>
void add(int ,int);// function prototype
void main()
{
int a=5,b=6;
int *p,*q; // pointer variable
p=&a; // assign the address of variable a to pointer variable p
q=&b;//assign the address of variable b to pointer variable q
add(*p,*q);
}
void add(int *p,int *q)
{
int sum=0;
sum=*p+*q;
printf("sum of two number =%d",sum);
}
example 2 swapping of two number using intermediate variable
#include<stdio.h>
void add(int ,int);// function prototype
void main()
{
int a=10,b=20;
int *p,*q; // pointer variable
p=&a; // assign the address of variable a to pointer variable p
q=&b;//assign the address of variable b to pointer variable q
printf(" Before swapping a=%d & b=%d ",a,b);
swap(*p,*q);
}
void swap(int *p,int *q)
{
int *temp;
temp=p;
p=q;
q=temp;
printf("After swapping a=%d & b=%d ",p,q);
}
output
Before swapping a=10 & b=20
After swapping a=20 & b=10
example 2 swapping of two number without using intermediate variable
#include<stdio.h>
void add(int ,int);// function prototype
void main()
{
int a=10,b=20;
printf(" Before swapping a=%d & b=%d ",a,b);
swap(&a,&b); //call by Address
}
void swap(int *p,int *q)
{
*p=*p+*q;
*q=*P-*q;
*p=*P-*q;
printf("After swapping a=%d & b=%d ",p,q);
}
output
Before swapping a=10 & b=20
After swapping a=20 & b=10