Linked list
Introduction to Linked Lists
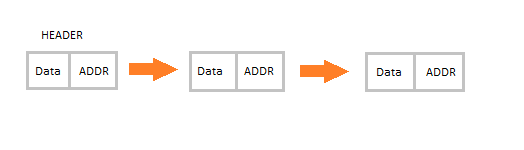
Linked List is a very commonly used linear data structure which consists of group of nodes in a sequence.
Each node holds its own data and the address of the next node hence forming a chain like structure.
Linked Lists are used to create trees and graphs.
Advantages of Linked Lists
- They are a dynamic in nature which allocates the memory when required.
- Insertion and deletion operations can be easily implemented.
- Stacks and queues can be easily executed.
- Linked List reduces the access time.
Disadvantages of Linked Lists
- The memory is wasted as pointers require extra memory for storage.
- No element can be accessed randomly; it has to access each node sequentially.
- Reverse Traversing is difficult in linked list.
Applications of Linked Lists
- Linked lists are used to implement stacks, queues, graphs, etc.
- Linked lists let you insert elements at the beginning and end of the list.
- In Linked Lists we don't need to know the size in advance.
Types of Linked Lists
There are 3 different implementations of Linked List available, they are:
- Singly Linked List
- Doubly Linked List
- Circular Linked List
Let's know more about them and how they are different from each other.
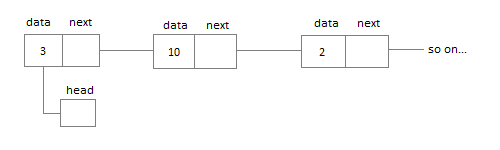
Singly Linked List
Singly linked lists contain nodes which have a datapart as well as an address part i.e.
next, which points to the next node in the sequence of nodes.
The operations we can perform on singly linked lists are insertion, deletion and traversal.
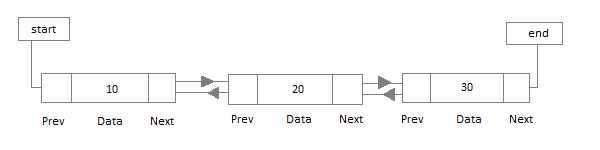
Doubly Linked List
In a doubly linked list, each node contains a datapart and two addresses, one for the previous node and one for the next node.
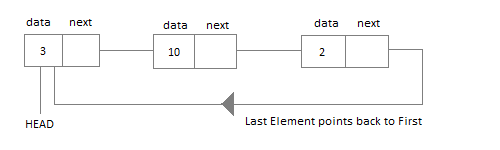
Circular Linked List
In circular linked list the last node of the list holds the address of the first node hence forming a circular chain.
We will learn about all the 3 types of linked list, one by one, in the next tutorials. So click on Next button, let's learn more about linked lists.